Risk Management
When developing its businesses, KTB prevents or mitigates damages that may be caused by risks through identification, balance, supervision, and management, so as to achieve reasonable risk pricing, to attain the balance between risk and performance. The implementation status of KTB risk management in 2024 is as follows:

Shaping the Risk Culture of KTB
Risk culture refers to an organized culture in which risk events or potential risks are managed through rigorous pre-incident controls and reporting procedures, proactive reporting by employees during the incident, and thorough investigation, improvement, and feedback following such events.

Organizational Structure of Risk Management
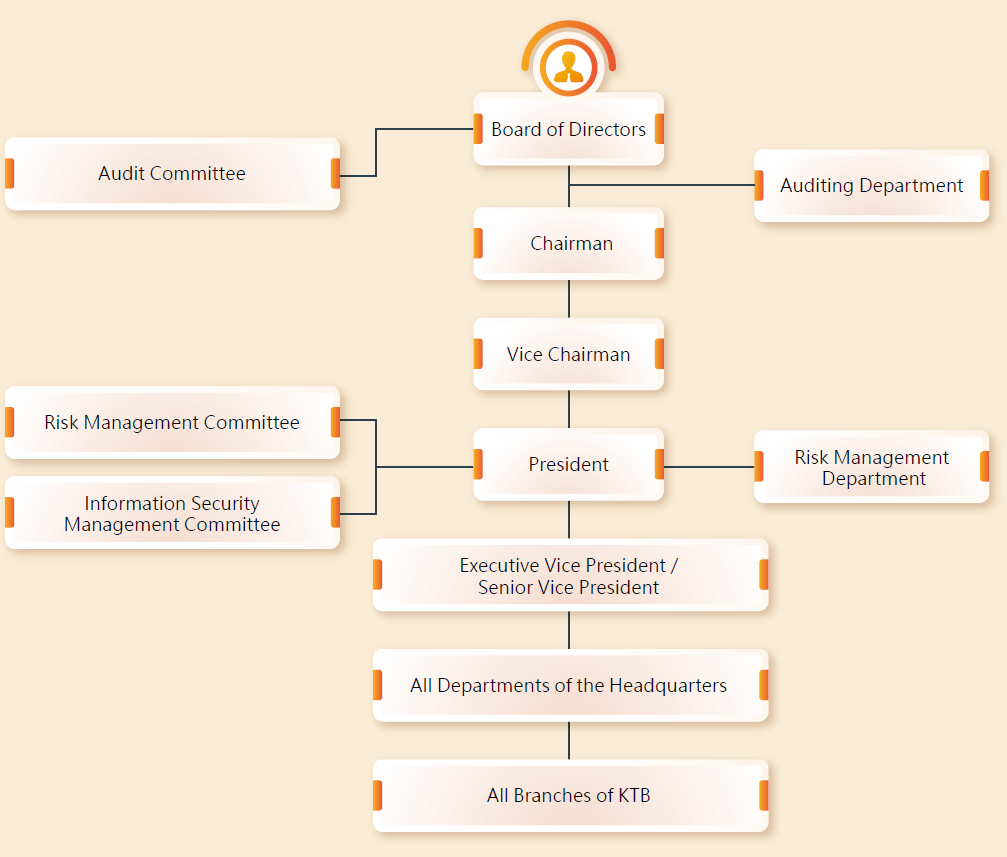
The Board of Directors is the highest authority in the risk management mechanism. It bears the ultimate responsibility for approving KTB's risk management policies and maintaining effective internal control policies. The functional committee - "Audit Committee" at the same level with the Board of Directors serves as the Supervision Unit. In addition, "Risk Management Committee" is set as passed by the Board of Directors, where, the President acts as Chairman, while heads of the departments such as the Risk Management Department, Treasury Department, Digital Service and Channel Management Department, Credit Assessment Department, Administration Management Department, International Banking Department, Compliance Department, Strategy and Operations Department and so as act as ex officio member. The committee holds meeting regularly every month, to guide addition and revision to risk management policy and make overall planning of various risk management matters of the whole company.
The "Risk Management Department" is responsible for executing and promoting the policies formulated by the Committee. The Department is also an independent unit that plans and supervises the overall risk management of KTB. At the beginning of every year, the head of the Risk Management Department is responsible for reporting various risk exposure conditions at the end of the previous year to the Audit Committee, and then to be passed upon resolution of the Board of Directors.
/upload/image/2025/09-03/9c8952772537466e90b95fb02f64b57b.png
The Company establishes and maintains the AML/CFT database in accordance with relevant information security regulations of the Company. The database primarily covers the following information:
1. When establishing a business relationship or conducting transactions with a customer, the Company must verify whether the customer, the senior management of the customers, beneficial owners, or other related parties are individuals, legal entities, or groups designated for sanctions under the Counter-Terrorism Financing Act, or are persons currently or formerly politically exposed persons in domestic or foreign governments or international organizations as defined under the Money Laundering Control Act.
2. The Accuity system is utilized to conduct verification operations through the "Customer Name Verification System" (LexisNexis-Accuity C-LINK). This system performs checks on the names of customers and related transaction parties. Information on Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs) and individuals associated with negative news, which has been collected but not published in the C-LINK list, is submitted to the manager of the Compliance Department for approval. Upon approval, the Compliance Department either processes the request independently or fills out a computer operation request form to seek assistance from the IT Department to update the list to the C-LINK system. Once completed, the Compliance Department reviews the integrity and accuracy of the data to enhance the completeness of the database.
3. Utilizing keyword to search for relevant negative news and examining whether it meets the relevant definitions. If matching negative news is found: in addition to retaining the search records, it should be confirmed whether the individuals involved in the negative news have business dealings with the Company, and information on relevant transactions should be reviewed to determine if there is a need to report suspicious transactions to the Ministry of Justice Investigation Bureau. Customer risk identification should be re-evaluated, and customer risk levels should be adjusted in a timely manner.
4. Establish a regulatory compliance platform to integrate relevant customer information for the purpose of querying, reviewing, or assessing the effectiveness of the Company's implementation.

Risk Management Policies and Objectives
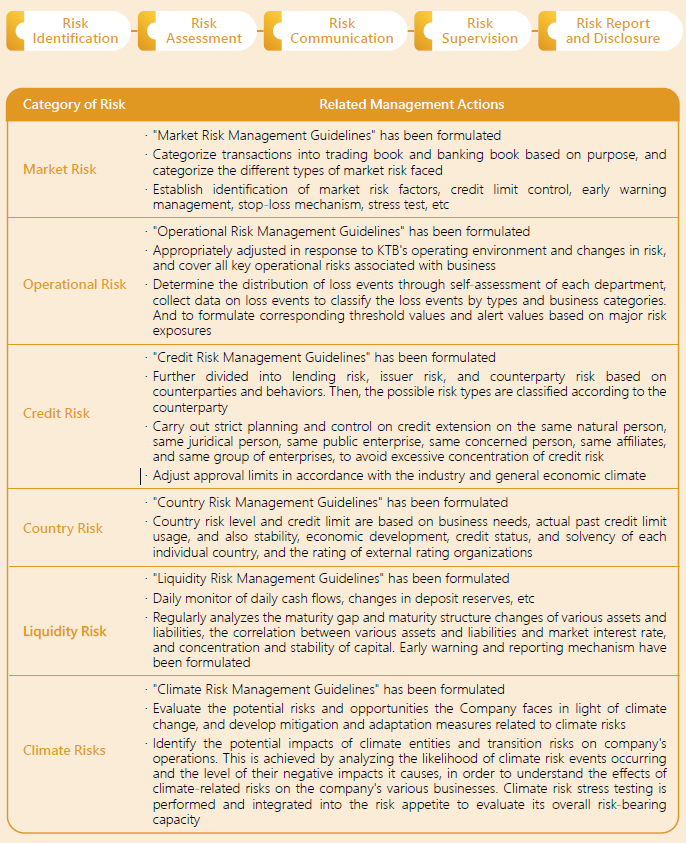
In order to ensure sustainable management and capital security, KTB clearly specifies the objectives and procedures of risk management based on the risk management policies approved by the Board of Directors. Thereby, KTB establishes effective risk management mechanisms to assess and monitor its risk-bearing capacity, the current status of risk already incurred, and to determine its risk response strategies. Moreover, KTB has established a capital adequacy assessment process that takes into consideration the risk status in order to maintain capital adequacy based on business growth, and to prevent risk concentration and ensure that the entire Bank's risk remains within the risk appetite. In addition, KTB conducts appropriate overall capital allocation to establish management measures for a variety of business risks considering our overall risk exposure and includes all risks on and off the balance sheet in the scope of risk management. The scope of risk management includes: credit risk, market risk, operational risk, liquidity risk, country risk, climate risk, and other risks. The management standards and regulations are formulated according to the different risks, specifying the management countermeasures, organizational structure and responsibilities, and management procedures for different risks.
Risk Management Mechanisms
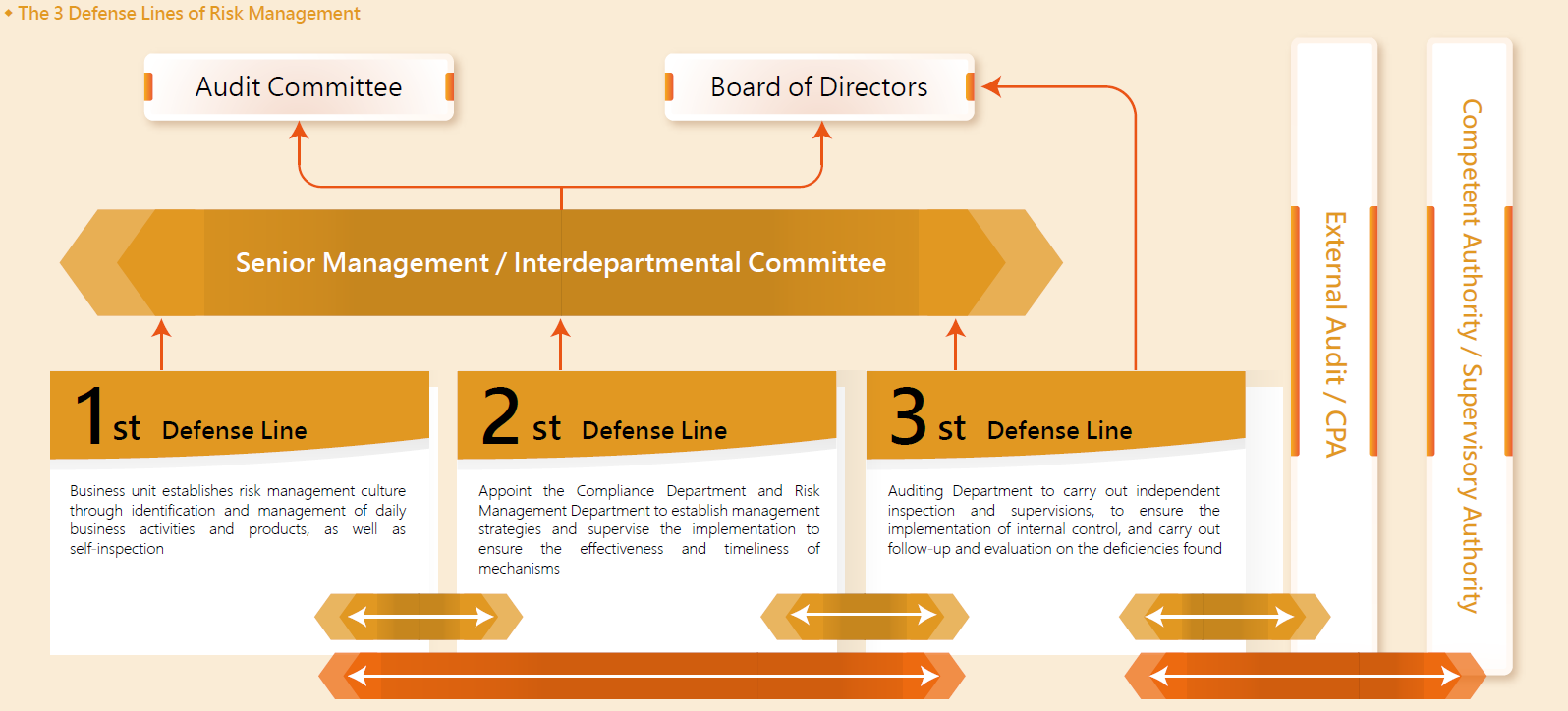
Risk management is the responsibility of all personnel in KTB. Through the 3 defense lines of internal control and various risk management procedures, KTB has established a comprehensive risk protection to ensure that all business risks can be controlled timely and effectively.
Risk Appetite Process/Framework
The Company's risk appetite refers to the overall risk that the Company is willing and able to bear in its operations. According to the "Regulations Governing the Capital Adequacy and Capital Category of Banks," this serves as a measuring indicator for determining whether to expand or downsize businesses. The Company shall, under the minimum statutory capital requirements, consider the overall risk status of the Company and, based on the changes in the capital adequacy ratio, the needs of the Company's various business developments, the Company’s business characteristics and the methodologies established by the supervisory authorities, the Company shall calculate potential unexpected losses from various types of risks under its current asset and operational status. In addition, the Company shall allocate corresponding capital in response to these risks. Furthermore, the overall capital allocation and capital adequacy shall be analyzed and assessed by category of risks, which shall be reviewed at least once a year. In the event of any significant changes in strategy or operating environment that may affect the methodology and assumptions of the evaluation process, a timely review and revision should be conducted.
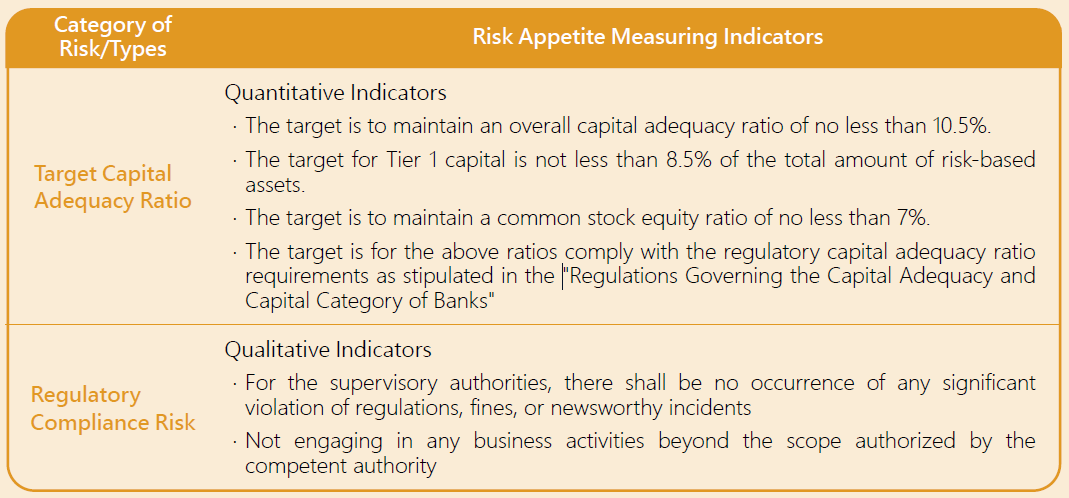
◆ Risk Management Procedures and Categories
The Company collects various risk factors regarding various financial products or services, which shall be used to identify relevant risks that might influence corporate sustainability. The Company formulates quantitative or qualitative standards in accordance with requirements and criteria of the competent authority to establish risk assessment indicators, thus serving as the basis for management decision-making, performance evaluation and so on. Each department abides by various measures and criteria to control risk of the business under their jurisdiction, and provides assistance in identifying and evaluating whether the risk control method is appropriate or not. The Risk Management Department performs independent monitoring of important projects or integration risk, and reviews and amends KTB's risk management goals and practical operations, so as to achieve dynamic prevention and control of risk expansion. In addition, the Risk Management Department is responsible for preparing risk control report and disclosing relevant information regularly.
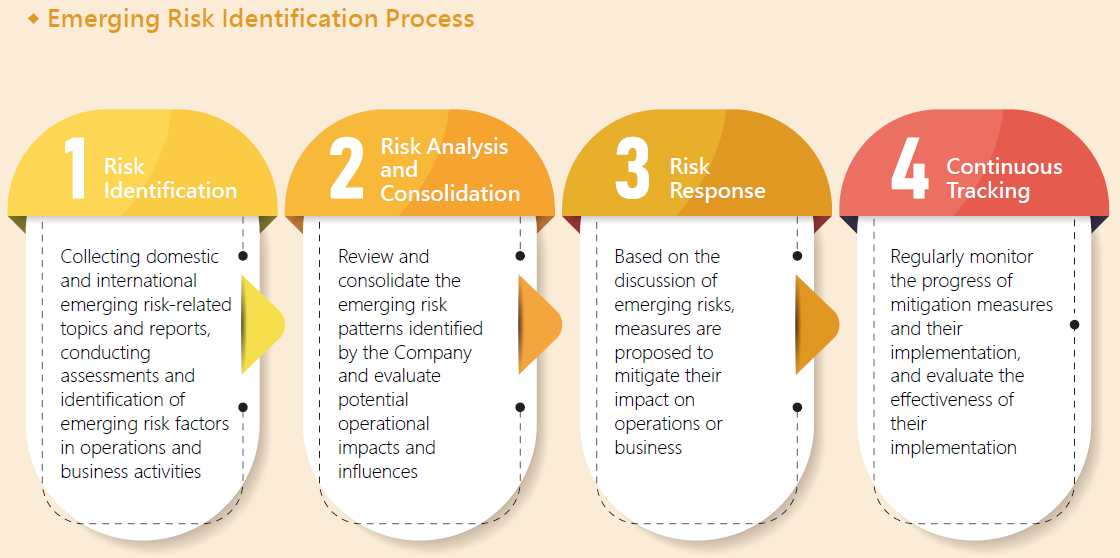
Emerging Risks
There is a recognition of both long and short-term risks. The rapidly worsening environmental risks, alongside societal polarization, geopolitical conflicts, and the rapid advancement of AI technology, all contributing to heightened uncertainty in global operations. In this global wave of change, the financial industry will be highly affected. In response to these challenges, KTB has not only established robust risk management mechanisms but also prioritized emerging risks as areas of focus, enabling the Bank to keep abreast of global developments, assessing the pros and cons for its operations and management planning, and continuously gathering risk reports from leading global institutions and address issues of concern from various stakeholders. By staying vigilant and proactive, the Bank can identify the latest trends in emerging risks and implement effective strategies to address them.
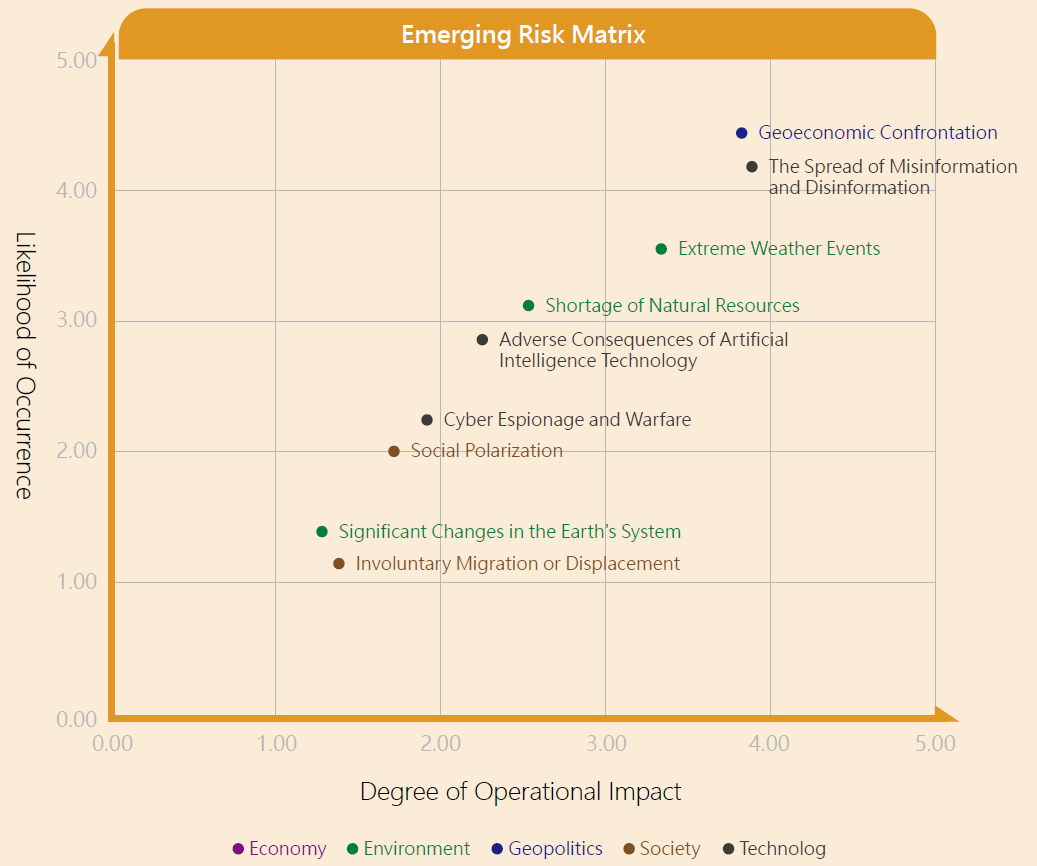
Analysis of emerging risk factors for KTB, taking into account the World Economic Forum's "The Global Risks Report 2025," evaluates five major categories of risk factors: economic, environmental, geopolitical, social, and technological, based on "likelihood of occurrence" and "impact severity." Three key emerging risks that may have a long-term impact in the future are identified, and corresponding response measures are proposed.
◆ Emerging Risk Matrix
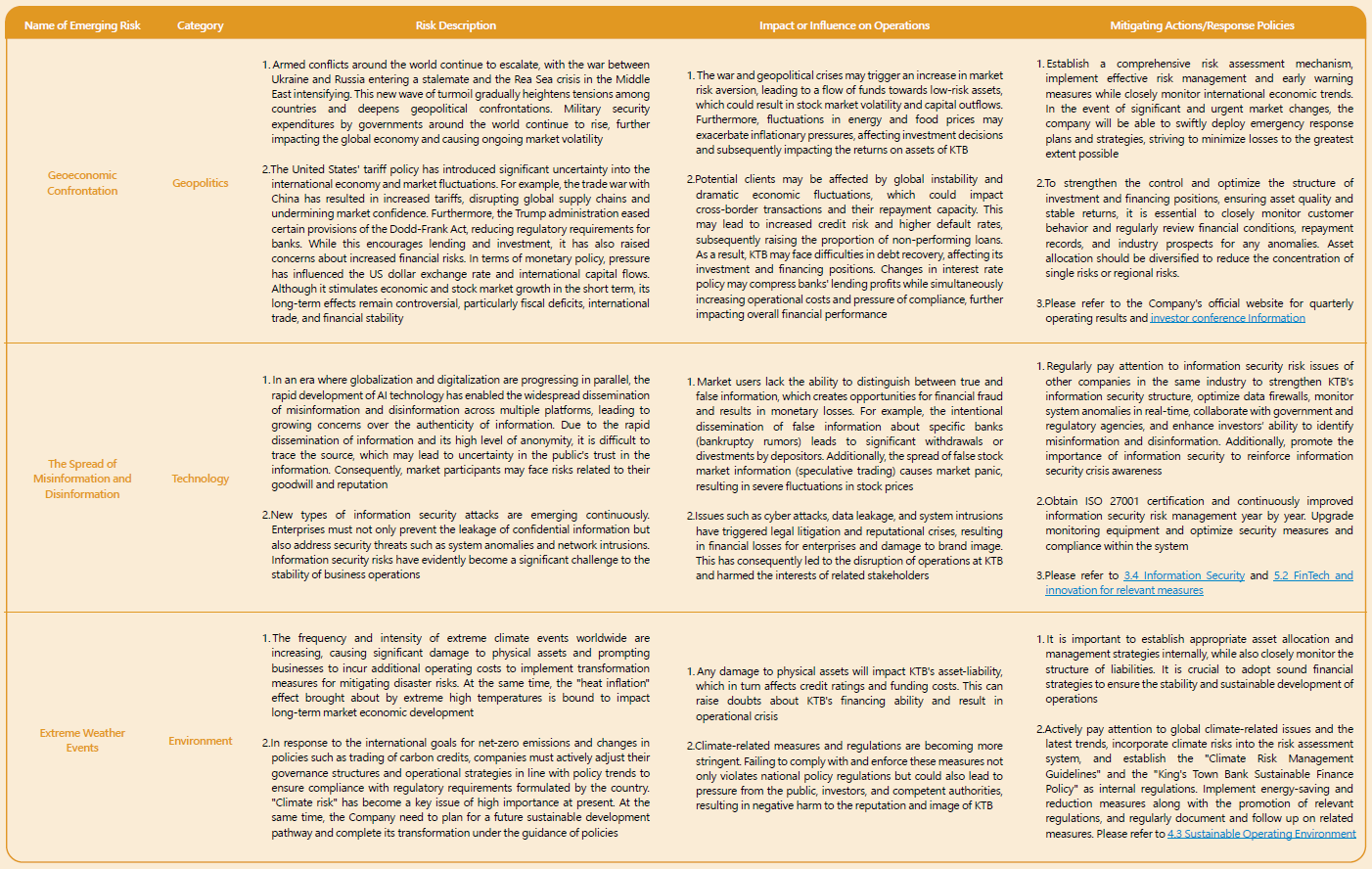
The emerging risks of the Company are assessed based on the "degree of operational impact" and "likelihood of occurrence." 9 major emerging risk factors have been identified: geo-economic confrontation, involuntary migration or displacement, social polarization, spread of misinformation and disinformation, cyber espionage and warfare, adverse consequences of AI technology, natural resource scarcity and extreme weather events. Among these, the emerging risks with the greatest impact are "geo-economic confrontation" and "the spread of misinformation and disinformation." In light of this, measures have been developed to strengthen the Company's operations and resilience in addressing these risks.